Natural gas is a critical energy source, but it often contains hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), a toxic and corrosive impurity. Removing H₂S—known as “sweetening”—is essential to meet pipeline specifications (typically <4 ppm), protect infrastructure, and comply with environmental regulations. The importance of H2S removal cannot be overstated in today’s energy landscape.
As of early 2026, innovations focus on sustainability, energy efficiency, and value recovery amid rising natural gas demand and stricter emissions rules. Key advancements include membrane technologies, electrochemical processes, and improved scavengers.
Recent advancements in technology have significantly improved the efficiency of H2S removal processes.
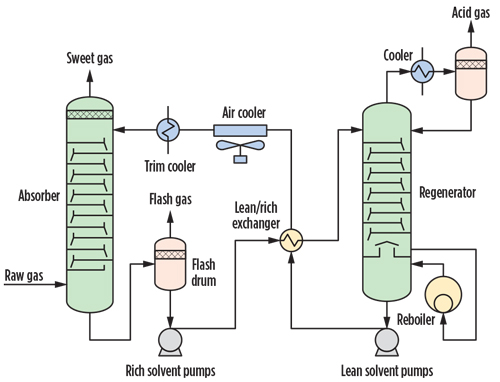
Traditional Methods
Amine-based absorption remains dominant, using solvents like MDEA to capture H₂S, followed by regeneration and Claus process for sulfur recovery. These methods are reliable but energy-intensive with potential waste issues.
Alternatives include solid adsorbents (e.g., iron sponge) and biological processes using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria.
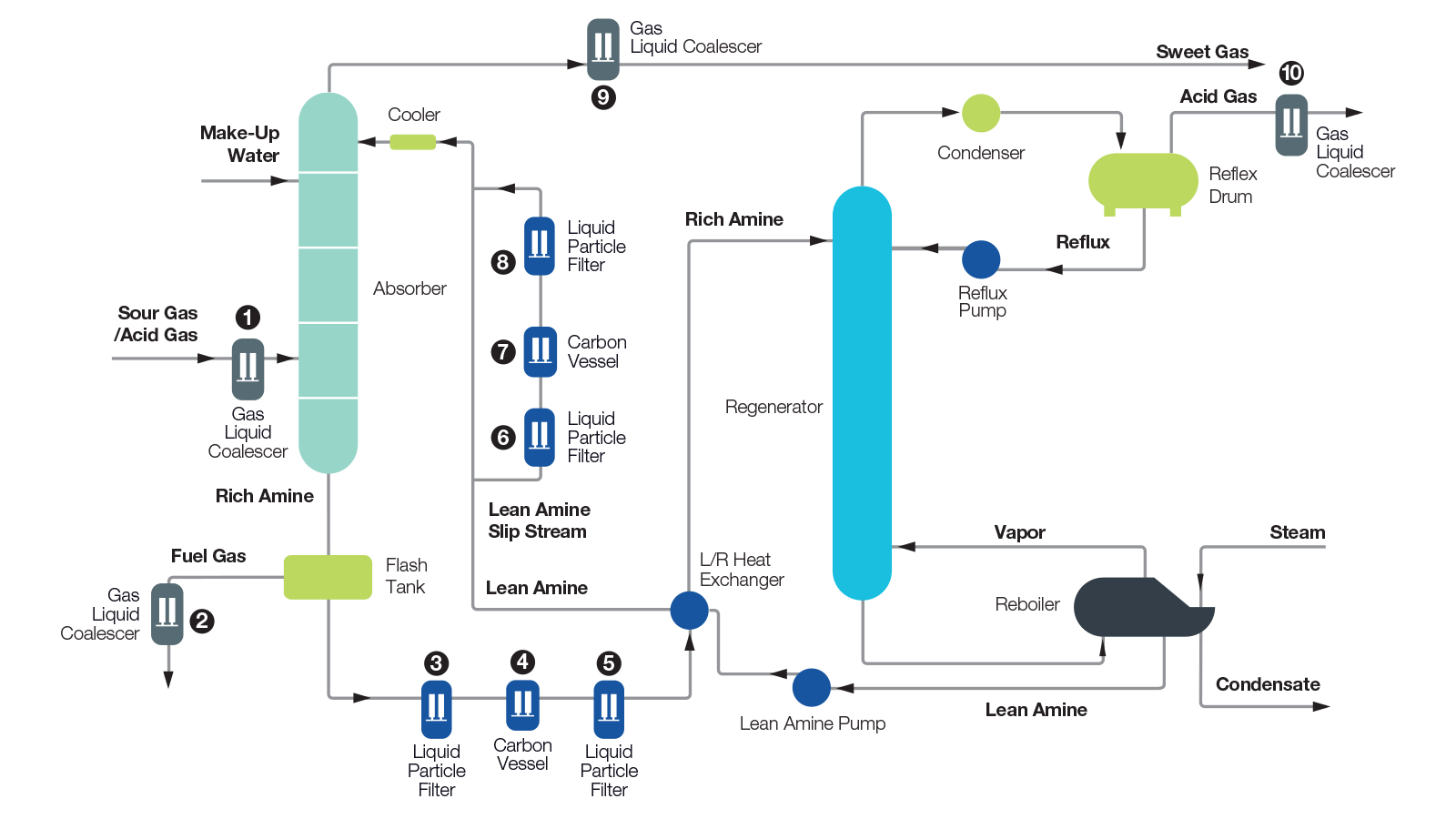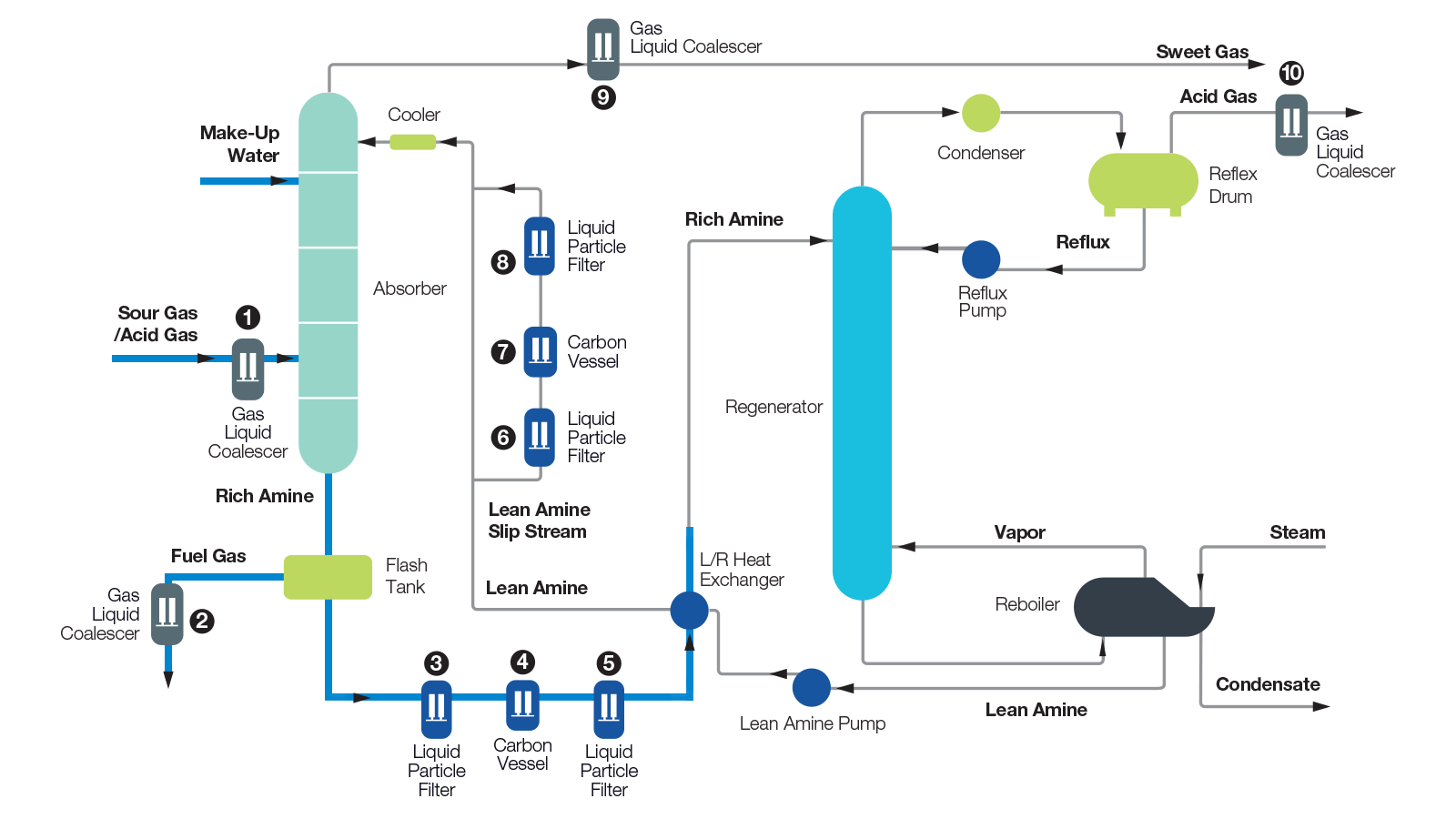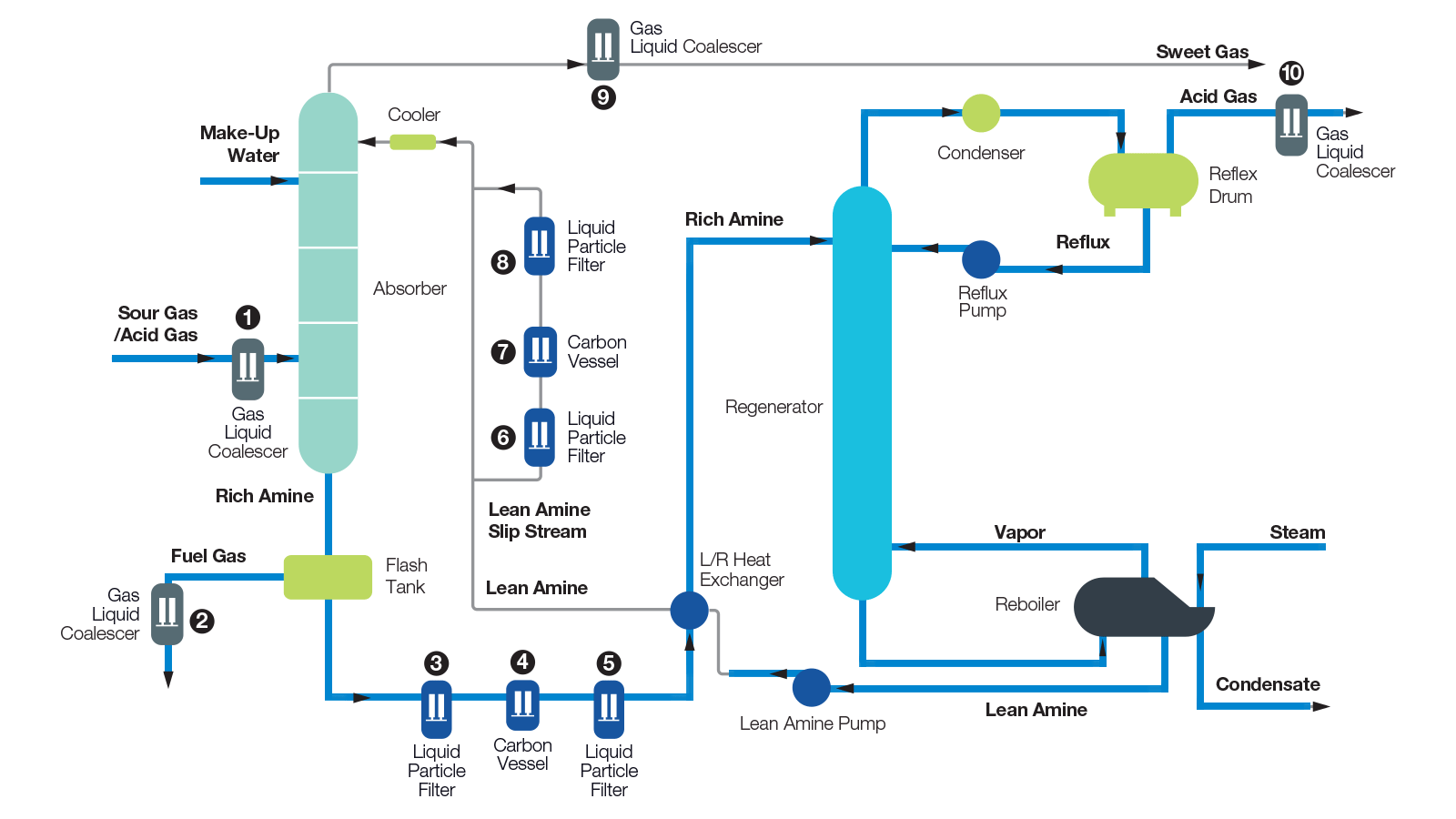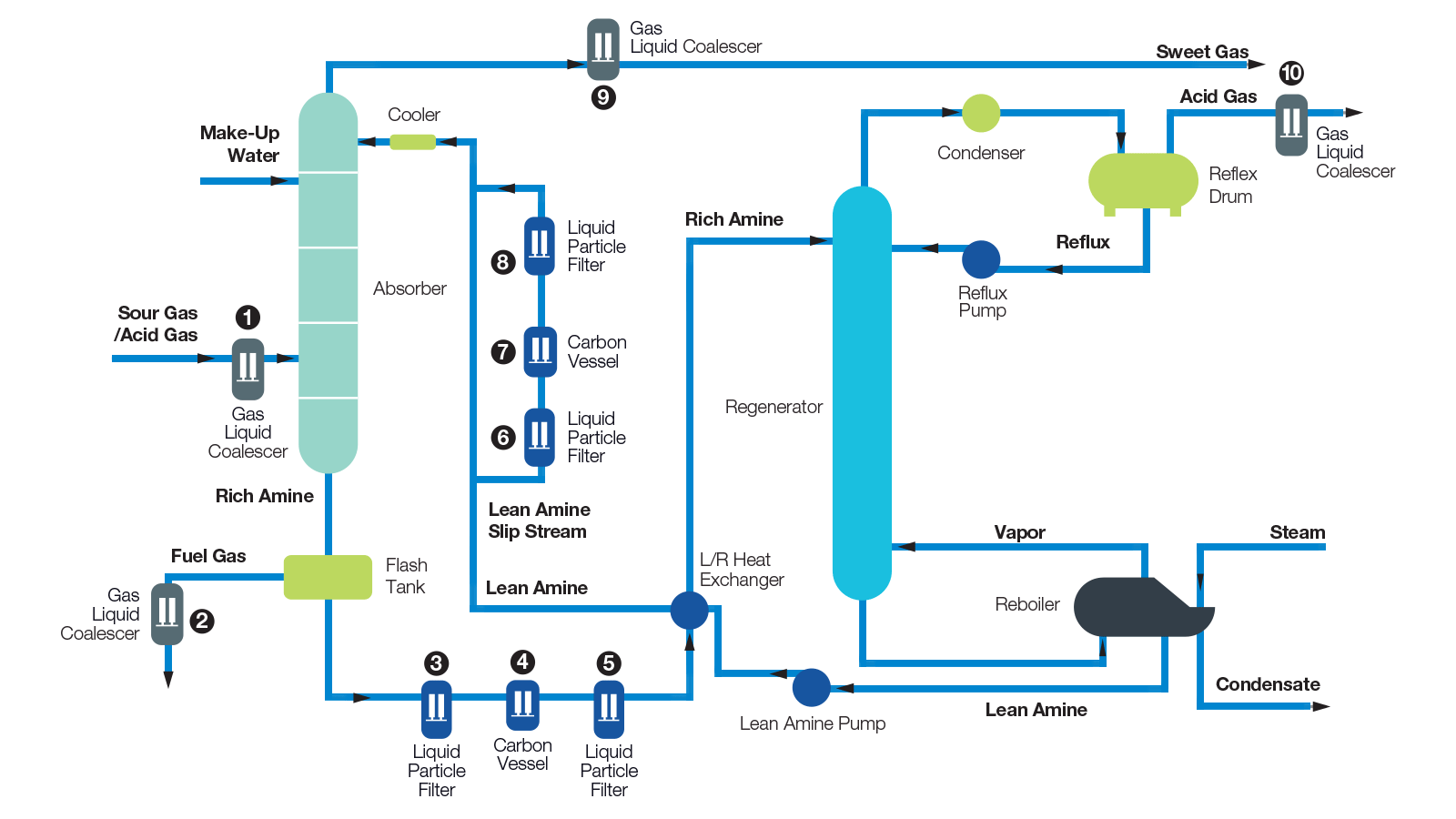
Emerging Membrane Technologies
Membrane separation offers low-energy, modular solutions. Recent systems like MTR’s SourSep™ enable bulk H₂S removal (>75%) with reinjection of sour permeate, reducing downstream load.
Advanced materials, including cellulose triacetate (CTA) hollow fibers and mixed-matrix membranes, handle high H₂S concentrations while maintaining hydrocarbon recovery.
Electrochemical Innovations
A breakthrough in 2025 involves electrochemical deep oxidation of H₂S to value-added sulfates (e.g., K₂SO₄ or H₂SO₄) under mild conditions. This uses in-situ generated H₂O₂ to oxidize sulfide, achieving high conversion and selectivity while reducing H₂S to <15 ppm.
Benefits include lower energy use than Claus, integration with renewables, and economic gains from fertilizer byproducts.

Regenerative Scavengers and Hybrid Solutions
Non-triazine scavengers and nanofluid-based systems enhance efficiency. Hybrid approaches combine membranes with absorption or biological methods for optimized performance.
Research also explores MOFs, ionic liquids, and microbial enhancements for selective removal.
Market Trends and Outlook
The H₂S removal market grows with sour gas production and LNG demand. North America leads, while Asia-Pacific expands rapidly. By 2030, membranes and electrochemical methods could claim significant share, driven by decarbonization.
Conclusion
H₂S removal technologies evolve toward greener, more efficient solutions. Electrochemical valorization and advanced membranes promise to transform sour gas processing, supporting a sustainable energy future.